Why This December Cold Snap Was a Heating Wake-Up Call
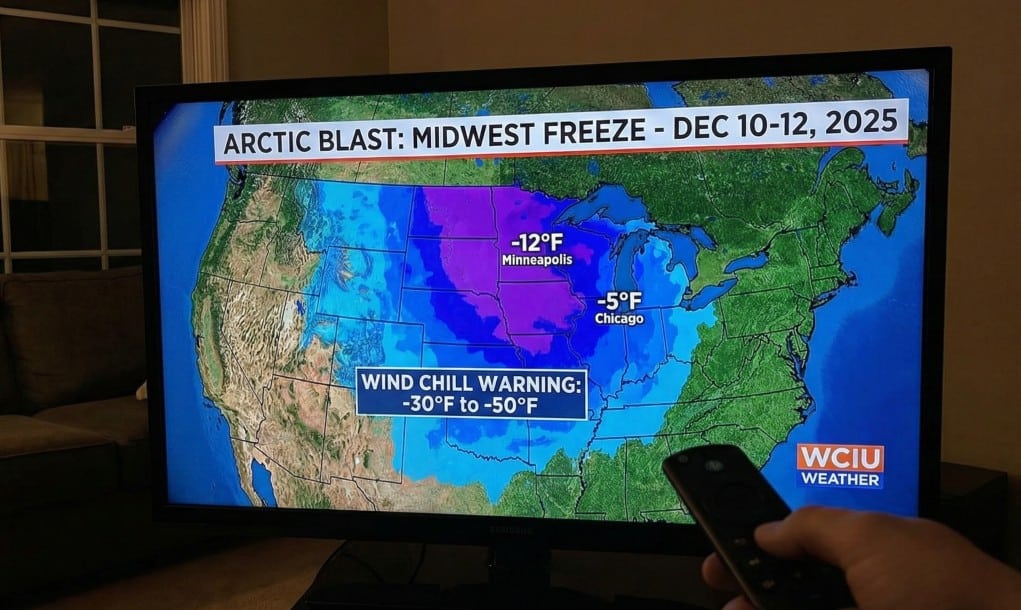
The recent December cold snap caught millions of homeowners off guard. Temperatures dropped fast, stayed low, and pushed heating systems well beyond what many were prepared for. In large parts of the country, furnaces ran nonstop, heat pumps struggled, and backup systems were tested for the first time in years. For many households, the experience was uncomfortable. For others, it was damaging and expensive.
What made this event stand out was not just how cold it became, but how quickly conditions changed. Homes that seemed perfectly fine in early winter suddenly faced frozen pipes, uneven heating, and complete system failures. In many cases, the warning signs were there long before the freeze arrived. They were simply easy to ignore during milder seasons.
This event served as a clear reminder that heating systems are not set-it-and-forget-it appliances. Many homeowners only think about their equipment when it stops working, yet routine professional heating maintenance can identify issues early and prevent mid-winter failures. They are mechanical systems that age, wear down, and lose efficiency over time. When extreme weather arrives, small problems turn into major breakdowns. The goal of this article is to explain why that happens, what homeowners can learn from it, and how to prepare before the next severe winter event.
Why Extreme Cold Exposes Heating Weaknesses
Severe winter weather places stress on every part of a heating system. Components that operate fine during normal conditions may fail once they are pushed to their limits. This is especially true for systems that have skipped routine service or are nearing the end of their lifespan.
One of the most common issues during a cold snap is extended run time. Furnaces and boilers are designed to cycle on and off. When temperatures stay far below normal, systems run longer and more often. This increases wear on motors, igniters, and control boards. Any part that is already weakened becomes far more likely to fail.
Fuel delivery can also become a problem. Natural gas pressure fluctuations, frozen propane regulators, and oil line issues are more common during prolonged cold. Even electric systems are affected, as higher demand can strain older wiring or expose failing breakers.
The Hidden Role of Maintenance
Many heating failures during extreme cold are not sudden or random. In fact, technicians who specialize in residential heating repair often see the same preventable problems resurface during every major freeze. They are the result of deferred maintenance. Dirty burners, worn belts, cracked heat exchangers, and clogged filters rarely cause immediate shutdowns in mild weather. During intense cold, those same issues can bring a system to a halt.
Annual maintenance allows technicians to catch these problems early. It also ensures that safety controls are working correctly. During heavy usage, safety switches are triggered more often. If they are faulty or improperly calibrated, the system may shut down repeatedly or lock out completely.
Another overlooked factor is airflow. Blocked vents, dirty filters, and undersized ductwork reduce a system’s ability to distribute heat evenly. During extreme conditions, this leads to cold rooms, overheating components, and higher energy bills.
Why Older Systems Struggle the Most
Age plays a major role in how a heating system responds to severe weather. Most furnaces and boilers are built to last 15 to 20 years. As systems age, efficiency declines and internal components weaken. Replacement parts may also become harder to find.
During a cold snap, older systems often fail in predictable ways. Homeowners who rely on aging equipment frequently end up needing emergency heating repair when systems can no longer keep up with demand. Blower motors overheat, heat exchangers crack, and control boards stop responding. Even if repairs are possible, repeated breakdowns during winter usually signal that replacement should be considered.
Modern systems are designed with better diagnostics, variable-speed operation, and higher efficiency ratings. They adjust more smoothly to changing demand and place less strain on individual components. While no system is immune to extreme cold, newer equipment typically handles it more reliably.
Insulation and Heat Loss Matter More Than You Think
Heating performance is not just about the equipment itself. The condition of the home plays a major role. Poor insulation, air leaks, and outdated windows force heating systems to work harder than necessary.
During severe winter weather, heat loss becomes far more noticeable. Warm air escapes through attics, crawl spaces, and poorly sealed doors. Cold air infiltrates through gaps and cracks. The heating system runs longer trying to compensate, increasing the risk of failure.
Improving insulation and sealing air leaks reduces strain on the system. Pairing these upgrades with routine heating system tune-ups helps improve comfort while extending equipment life. It also improves comfort and lowers energy costs year-round. These upgrades are often more affordable than homeowners expect and can significantly extend the life of heating equipment.
Emergency Breakdowns and What They Really Cost
When heating systems fail during extreme cold, the consequences go beyond discomfort. Frozen pipes can burst and cause major water damage. Space heaters increase fire risk. Hotel stays and emergency repairs add up quickly.
Emergency service is also more limited during widespread cold events. When thousands of systems fail at once, response times increase. Homeowners who already have a relationship with a service provider are often prioritized, while others may wait days for repairs.
Planning ahead reduces these risks. Establishing a relationship with a trusted local provider for heating services in Colorado often means faster response times and fewer surprises during widespread winter emergencies. Knowing the condition of your system, scheduling maintenance, and addressing small issues early can prevent emergency situations when demand is highest.
Warning Signs Homeowners Often Miss
Many homeowners look back after a breakdown and realize the system was warning them. Unusual noises, short cycling, uneven heating, rising utility bills, and frequent thermostat adjustments are all signs of trouble.
During normal weather, these issues may seem minor. During a cold snap, they can turn into system failure. Paying attention to these signs and addressing them early is one of the best ways to avoid emergency repairs.
Another common warning sign is system age. If your heating equipment is over 15 years old and has required frequent repairs, it may not be reliable during extreme conditions. Planning replacement on your timeline is far better than doing it during a winter emergency.
Preparing for the Next Severe Winter Event
Extreme cold events are becoming more unpredictable. Preparation is no longer optional. Homeowners should start with a professional system evaluation before winter arrives. This includes checking safety controls, heat output, airflow, and overall system condition.
Simple steps also make a difference. Replacing filters regularly, keeping vents clear, sealing air leaks, and testing thermostats all improve reliability. Backup plans, such as knowing where the main water shutoff is located, can also reduce damage if a failure occurs.
Preparation does not eliminate risk, but it greatly reduces it. Homeowners looking to better understand how heating systems perform in extreme winter conditions can also review guidance from the U.S. Department of Energy on home heating efficiency and cold-weather performance. Homes that weather severe cold successfully usually have one thing in common: proactive planning.
FAQs
Why did so many heating systems fail during this winter event?
Extreme cold pushes systems to run longer and harder than usual. Any existing wear, lack of maintenance, or airflow problems become much more likely to cause failure under these conditions.
Is my heating system too old to handle extreme cold?
Age alone does not guarantee failure, but older systems are more vulnerable. If your system is over 15 years old and has a history of repairs, it may struggle during severe winter weather.
Can maintenance really prevent emergency breakdowns?
Routine maintenance significantly reduces the risk. It allows technicians to identify worn parts, safety issues, and efficiency problems before they cause system shutdowns.

What should I do if my heat goes out during extreme cold?
First, check basic issues such as thermostat settings and circuit breakers. If the system does not restart quickly, call for professional service and take steps to protect pipes from freezing.
How early should I prepare for winter heating season?
Ideally, systems should be inspected and serviced in early fall. This allows time for repairs or upgrades before cold weather arrives and demand increases.
Are newer heating systems better for extreme weather?
Newer systems are generally more efficient and reliable. They are designed to handle variable demand and often include advanced safety and diagnostic features that help during extreme conditions.